胚胎植入前诊断(PGT-M / SR)是指
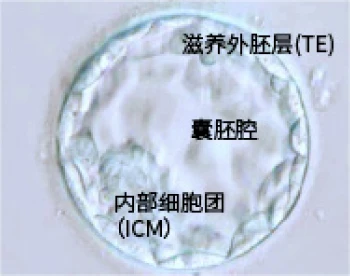
About胚胎植入前单基因/染色体结构重排检测(Preimplantation Genetic Testing for Monogenic/Structural Rearrangements;PGT-M/SR)是为了诊断特定遗传性疾病或染色体结构异常而进行的受精卵检测。该检测对象包括重度遗传性疾病以及被认为由平衡型染色体结构异常引起的习惯性流产。在受精后第5~7天,从囊胚的TE细胞(将来形成胎盘的部分)中采集一部分,提取并扩增DNA后进行分析。 本公司可使用医疗机构在实施着床辅助技术“TE去除”时所去除的TE细胞,进行PGT-M/SR(以下称为本法)以及PGT-A(染色体数目异常检测)。
已处理的遗传性疾病
除下列疾病外,我们还可应对其他疾病。详情请联系我们。
- 杜氏肌营养不良症
- 贝克肌营养不良症
- 福山型先天性肌营养不良症
- 福山型肌营养不良症
- 肌强直性(张力性)营养不良
- 脊髓小脑变性症
- 朱伯特综合症
- 亨廷顿病
- 肾上腺脑白质营养不良症
- 粘多糖贮积症Ⅱ型
- 先天性鱼鳞病
- I型神经纤维瘤病
- 视网膜母细胞瘤
- 奥尔波特综合征
- 成骨不全症
- 马凡综合征
- GJB2 基因突变导致的隐性遗传性耳聋
- 伴皮质下梗死和白质脑病的常染色体显性遗传性脑动脉病
- 腓骨肌萎缩症
- 围产期型低磷酸酯酶症
- 软骨发育不全症
- OTC缺乏症
- 法布瑞氏症
- 利氏病
- 脊髓性肌萎缩症
- 佩梅病
- 先天性肌病
- 成骨不全症Ⅱ型
- 成人型骨发育不良
- 限制性皮肤病
- 鸟氨酸氨甲酰转移酶缺乏症
- PDHC缺乏症(丙酮酸脱氢酶复合物缺乏症)(高乳酸高胆红素血症)
- 5,10-亚甲基四氢叶酸还原酶缺乏症
- L莱施-奈恩综合征(自毁容貌症)
- 戊二酸血症Ⅱ型
- X连锁遗传性脑积水
- 血液免疫
- 畸形综合征
- 染色体异常(可能生出患有严重遗传性疾病儿的染色体结构异常)
优点与缺点
Benefits & Risks优点
- 施行本方法可以降低患有因特定基因异常或染色体异常等引起的先天性疾病儿出生的可能性。
- 同时施行PGS检查,可以将不能妊娠的胚胎从移植胚胎中剔除,从而降低流产率并能防止不孕治疗中费用的过度支出和时间的浪费。
缺点
- TE细胞的切除,可能会引发囊胚破碎或发育停滞。由于采取细胞而诱发染色体异常的状况不会发生。
- 因诊断结果大致需要4周时间,所以选择施行本法的话就不可以进行新鲜胚胎移植。TE细胞切除后的囊胚会施行冷冻保存,等待诊断结果出来以后可以施行胚胎融解移植。
- 移植施行过PGD,PGS没有发现染色体异常的囊胚,经过怀孕到分娩,最终出生时发现孩子有染色体异常的状况偶尔也有发生。主要原因可能是检查用的TE细胞(将来长成胎盘的部分)和将来长成胎儿的细胞(ICM)的染色体不一致而导致的,另外也有可能是NGS所不能检测到的细微缺失的原因。
方法
Methods ⑴ 提供咨询服务和进行事先检查。
※首先请提交目标基因检测报告。在此基础上,我们将采用唾液(本人和家属)施行基因检测并提供咨询服务。
⑵ 施行取卵,显微授精(ICSI),囊胚培养。
⑶ 施行TE细胞活组织检查。(从囊胚上取一部分TE细胞)
⑷ 施行基因和染色体的解析。
关于结果
Test Results 检查结果报告会邮寄给本人。
如有任何问题,请通过电话,电子邮件或面谈联系我们。
申请与咨询请联系
接待时间:工作日 9:00–17:00 000-0000-0000
24小时受理 chinese_help@ogms.biz
【关于邮件咨询】
夜间,周末,节假日,新年及暑期休假期间收到的咨询,回复可能会延迟。根据咨询内容,有时需要较长时间才能提供答复。
【注意事项】
如果您设置了“只接收指定域名邮件”或“拒收电脑端邮件”,可能会导致无法接收邮件。
请更改设置以允许接收以下域名的邮件:
ogms.biz
